Software Installation
The purpose of this exercise is to get you set up with the software tools we’ll use in PIC16B, including Anaconda, git + GitHub, and Jekyll.
§1. Install and Configure Anaconda
An important part of PIC16B is navigating the Python package ecosystem.
We will do so using the Anaconda distribution of Python. Getting set up with Anaconda is a somewhat detailed process, outlined below.
You should follow these instructions even if you already have Anaconda installed. Uninstalling and reinstalling is recommended.
§a. Install Anaconda
You can find installers for Anaconda here. Choose the one appropriate to your operating system.
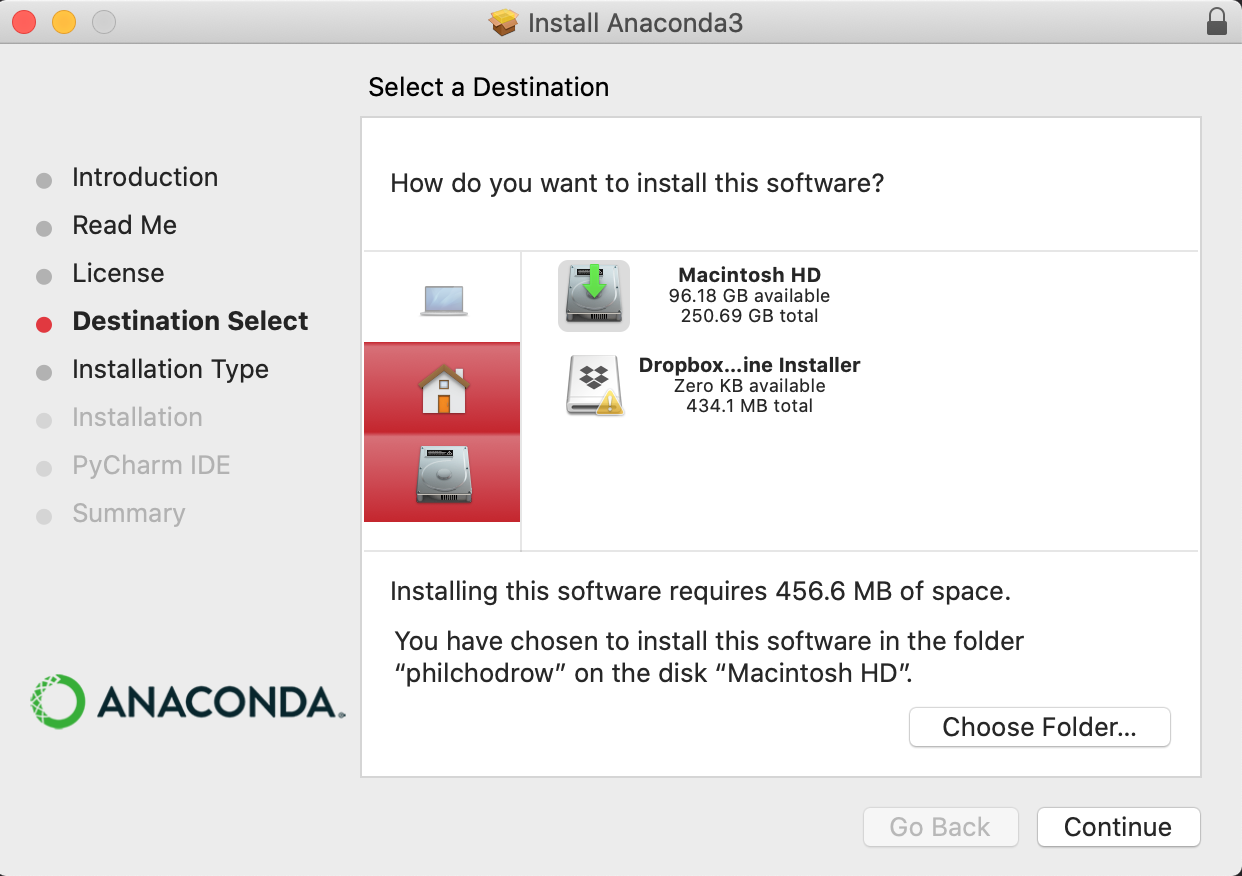
If installing on macOS, do not install Anaconda in the root-level opt directory. It is recommended that you install in the folder directly under your username. This is the same folder in which your “Downloads” folder exists. In some cases, Anaconda may suggest installing in a folder called opt under your username; this is fine.
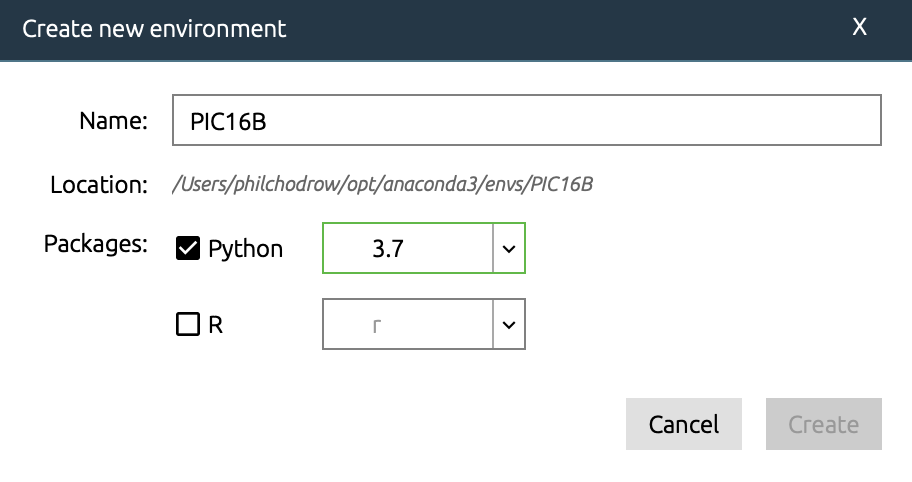
§b. Create the PIC16B Anaconda Environment
- Open Anaconda Navigator.
- Navigate to the Environments tab.
- Choose “Create.”
- Create a Python 3.7 or 3.8 environment named “PIC16B.”
§c. Install nb_conda
Still in the Environments tab, search for the nb_conda package on the right-hand side (you may need to update the index).
Check the box beside this package, and then click “Apply” to install.
§d. Install packages
While you’re here, you may also wish to install some other familiar packages, such as matplotlib and pandas (installing pandas automatically installs numpy). In the future, if you ever attempt to import a package and encounter an error, you should attempt to install it via the Environments tab.
In this course, we’ll primarily demonstrate TensorFlow using Google Colab, which has some significant benefits related to speed of computation. However, you can also try to install the tensorflow package via the package manager.
Note: If you want to use command lines to install Python packages in the future, try to follow prompts that look like
conda install --channel=conda-forge [package name]
rather than the ones that start with pip install. If this sentence didn’t make sense to you, you can ignore it and stick to using Anaconda navigator.
§e. Launch Jupyter Lab
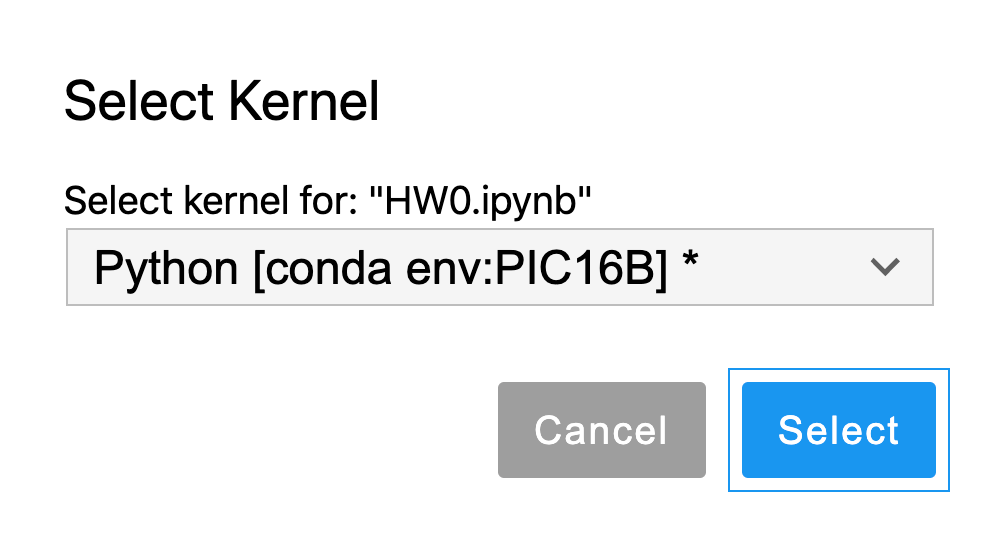
Now go back to the “Home” tab. Launch JupyterLab or Jupyter Notebook. You may need to install the app first.
Create a new Jupyter notebook. Change the kernel to the PIC16B environment that you created in Step §2
§f. Verify
Type the two lines below into your blank Jupyter Notebook and run them, adding in your name. If you do not encounter an error, then your setup was successful. Otherwise, contact the instructor or TA for help.
import pandas as pd
print("My name is [your name] and I installed Anaconda and TensorFlow")
§2. GitHub
Create an account on GitHub. You get a lot of free stuff as a student.
§3. GitHub Desktop
Download GitHub Desktop, a graphical client for working with git. If you do not use GitHub Desktop (or another graphical client), you will need to work with git from the command line.
Connect your GitHub Desktop app to your GitHub account.
§4. Install and verify Jekyll
In this course, we’ll use the Jekyll static website generator to create a simple, attractive website on which to host our homework and project submissions. Installation of Jekyll requires some minimal use of the command line (terminal), but the instructions will guide you through it.
- Install Jekyll on Windows. We recommend using the instructions under “Installation via Bash on Windows 10.”
- Install Jekyll on macOS
- Install Jekyll on Ubuntu or other Linux systems.
Once you’ve followed these instructions, verify your installation. To do so, run the following command in your terminal:
which ruby
ruby -v
jekyll -v
The terminal output should look something like this:
(base) zippy:~ harlinl$ which ruby
/Users/harlinl/.rbenv/shims/ruby
(base) zippy:~ harlinl$ ruby -v
ruby 2.7.0p0 (2019-12-25 revision 647ee6f091) [x86_64-darwin20]
(base) zippy:~ harlinl$ jekyll -v
jekyll 4.2.2
Your exact version number for jekyll may be different. If you see a version number of 4.0 or above printed, you are good to go! Nice work.
FAQ 1
If you’re using a mac, this is what worked for me:
- On your terminal, run
xcode-select --install -
Install
rbenvby following steps 1-4 in https://github.com/rbenv/rbenv#installation. - On your terminal, run these lines one at a time
rbenv install 2.7.0 rbenv local 2.7.0 gem install --user-install bundler jekyll
FAQ 2
Apparently there’s a lot of difficulty installing Jekyll with the newer Macbooks with M1 chip. Shruti says this link and commands helped. Please ask her for help if you have a Mac with M1 chip.
brew install readline openssl
rbenv install 2.7.2
gem install -n /usr/local/bin jekyll
FAQ 3
For the error “Could not locate Gemfile” in Windows, follow the steps in this link.
FAQ 4
Some users may need to run the following command after following the other steps in order for Jekyll to run correctly.
gem install --user-install ffi -- --enable-libffi-alloc
§5. (Recommended): Install a Text Editor
Text editors allow you to make modifications to plaintext files. They are useful for coding, writing, and any other tasks that require the manipulation of plaintext.
Jupyter Lab includes some basic text editor capabilities, but you might have a better experience with a dedicated text editor program. Visual Studio Code is my personal choice. Sublime Text and Atom are also popular. Some people also use Notepad++ but that might not be the best option for beginners. Beyond this course, if you expect to write a significant amount of code in your career then it is worthwhile to find a text editor that you like.
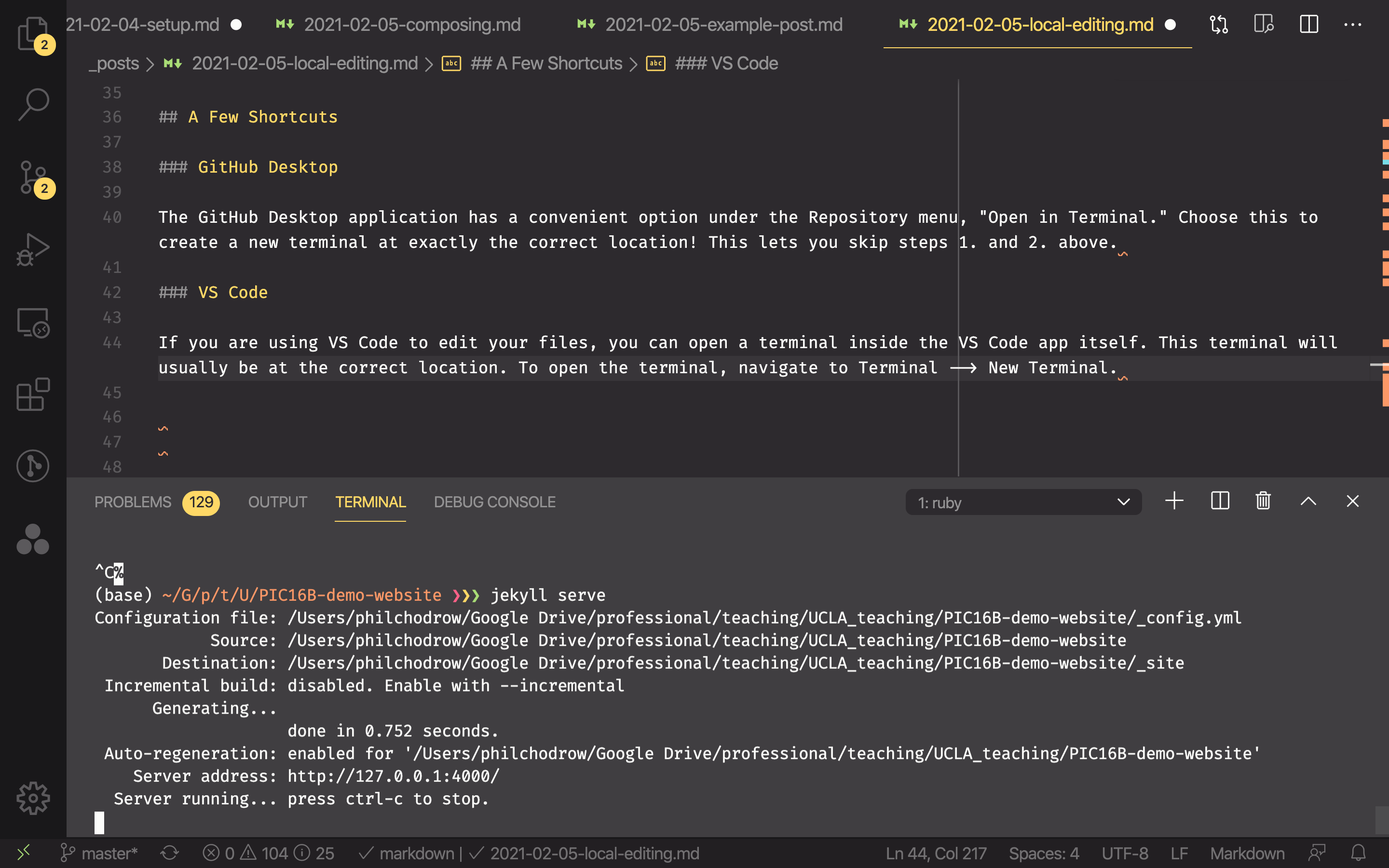 Blogging with Jekyll and Visual Studio Code.
Blogging with Jekyll and Visual Studio Code.
Once you’ve installed a text editor that you like, try opening it up and modifying a text file.
Next, try writing a simple Python file and running it from your editor. To do this, first paste the following into a file called my_script.py:
print("I can run Python scripts from my text editor!")
Then, open a terminal window from your editor. In the terminal, write python3 my_script.py and hit enter. You’ll need to ensure that your terminal is in the same location as the file my_script.py. We’ll learn more about how to use the terminal and text editor in an upcoming Discussion activity.